Git is an open-source program for version control of files, which is mainly used for programming in teams. This allows several people to work on a project without problems with different code versions. Git received additional hype through the upswing of so-called DevOps approaches in programming.
What is DevOps?
The central point of DevOps involves the team working together from the creation of a prototype to the live launch of the finished application and far beyond. For this purpose, various team roles are defined to ensure a smooth and fast process.
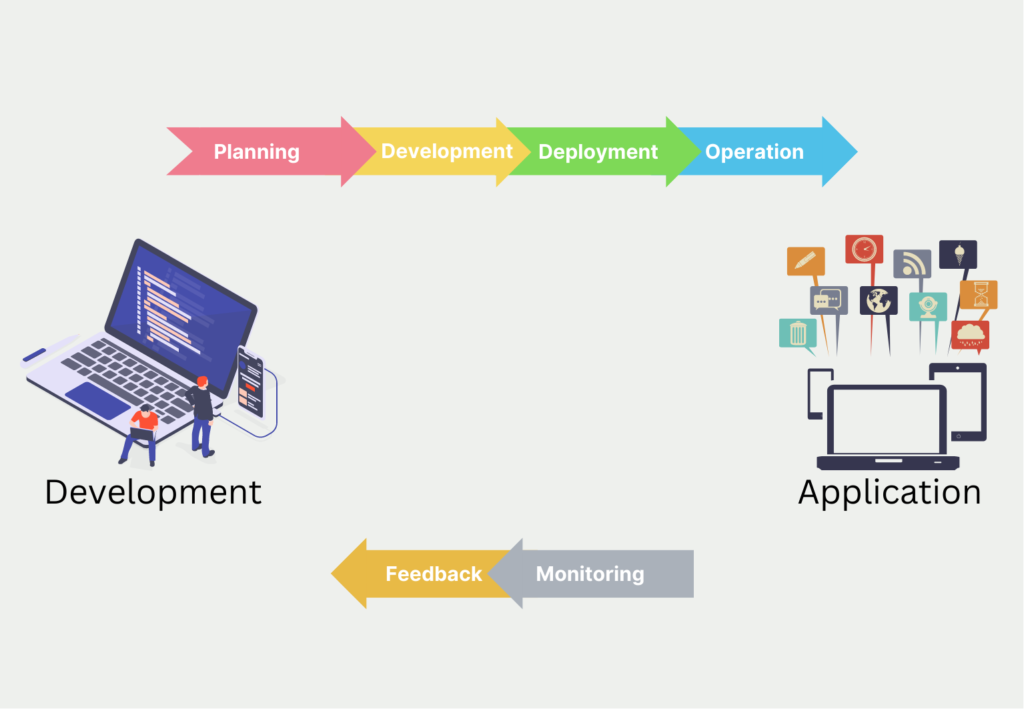
This approach differs from previous practices in that the development team and operations team now work closely together. Previously, applications were created by developers and once they went live, they were handed off to the operations team, which was tasked with ensuring the accessibility and performance of the service. However, valuable information is lost between the two teams, such as improvement suggestions from the operations team or know-how from the development team.
Depending on the application, experts from security or quality assurance can also be brought into the project team in addition to these departments. Especially if aspects from these areas are of particular importance for the project.
The team uses practices originally known from process automation that can also be applied to software development. The focus is on an endless loop of processes that are run through step by step.
What is a Version Control?
Version control is immensely important when working on programs in a team. Several people may be working on the same function in the code or on functions that influence each other since the output of one function is the input of another. Therefore, it must be ensured that once individual tasks have been completed, the functionality of the overall project is still ensured.
To manage these different versions of the same code, there are three types of version controls:
- Local: With local version control, a new directory is simply created on the computer, into which the files are then copied. This ensures that the old version can be used again as a fallback.
- Central: With central version control, this directory is located on a central server. Then the collaborating programmers can download the current state and download it to their devices. As soon as the changes have been made, the directory on the server can be overwritten or a version can be created.
- Decentralized: The decentralized version control acts relatively similar to the centralized one with the difference that each programmer always downloads the complete(!) directory locally, in order to be able to make the changes. Thus the current state is decentralized with all team members.
What terms do you use in the Git environment?
Before we can go into detail about how to implement concrete programming projects using Git, we first need to define a few terms that are commonly used in this environment:
- The repository is a directory that contains the current status of the project, as well as all changes. In addition, there is the remote repository, which is stored locally with the developer, if new components are to be added.
- With each Commit, the current conditions are stored as a new version. It is thus a kind of storing of changes in the local Repository.
- With a push request, one overwrites the state of another repository.
- In the Branches, new components can be developed at the same time.
- When different branches are merged, this is referred to as “merging“.
How does Git work in programming?
Git is so-called decentralized version control. Each programmer has a copy of the current repository, i.e. the directory, stored on his local computer. With this local copy, the programmer can then either create new files in the project or modify existing ones. At the same time, he can also test locally and ensure that the local changes do not affect the functionality of the overall program.
After downloading the latest version, you create a branch in which the new development is programmed. As soon as you have made and tested the changes, you can commit them, i.e. save them. Afterward, however, you cannot simply upload the latest version directly back into the repository.
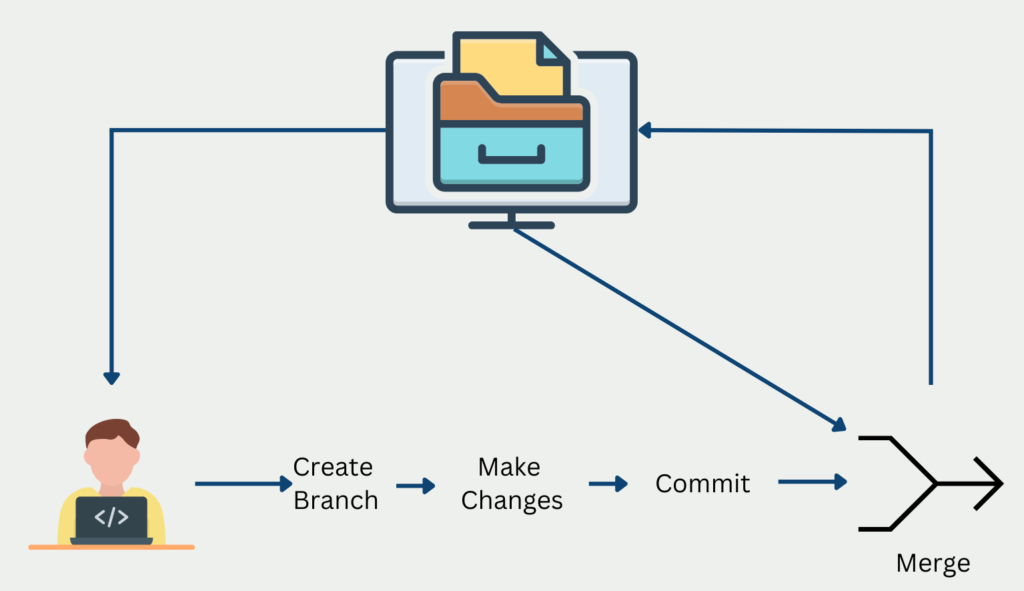
In the meantime between the last download of the repository and the implementation of the change, other team members may have overwritten the repository. That’s why you perform a pull request to have the latest state of the repository on your local machine. Then you can “merge” this new state with the changes in the branch. In doing so, you make sure that your own changes do not have any negative effects on the work of the other team members. Only then can you save your status in the repository with a push request.
What are the advantages of Git?
The decentralized structure of Git ensures that the data cannot actually be lost. The fact that each team member has a version of the repository stored on their computer should ensure that the project is always reasonably up-to-date. With centralized version control, on the other hand, a simple server failure can lead to the loss of the entire repository.
The push requests do not directly overwrite the repository, but only create new versions, which can of course also be restored at a later time. Thus Git offers the possibility to return to old versions if this is desired.
Git’s performance is very high compared to competitors because it is extremely efficient with storage and performance capacities.
What are the Git hosting platforms?
Git is a distributed version control system that allows users to track changes to code, collaborate with others, and manage code repositories. One of the most popular features of Git is the ability to host code repositories on multiple platforms. These platforms provide users with a central place to store and manage their code, as well as a variety of features that make it easier to collaborate with others. Here are some of the most popular Git hosting platforms:
- GitHub: This website is the largest Git hosting platform with over 56 million repositories as of 2021. It offers users a wide range of features, including code review, issue tracking, and project management tools. GitHub also offers a social aspect: users can follow each other, tag repositories, and contribute to open source projects.
- GitLab: GitLab is another popular Git hosting platform that offers users similar features to GitHub. However, it offers some unique features, such as built-in continuous integration and deployment, and better control over the deployment process.
- Bitbucket: Bitbucket is a Git hosting platform owned by Atlassian, the maker of Jira and Confluence. It offers users similar features to the previous platforms, such as code review and issue tracking tools. However, Bitbucket also offers some unique features, such as support for Git and Mercurial repositories and built-in continuous deployment.
- Azure DevOps: Azure DevOps is a suite of tools provided by Microsoft that includes a Git hosting platform. Azure DevOps provides users with a wide range of features, including continuous integration and deployment, project management tools and support for multiple programming languages.
- SourceForge: SourceForge is one of the oldest Git hosting platforms, dating back to the early days of open source software. While it doesn’t have as many features as some of the other platforms, it does provide users with a centralized place to store and manage their code.
These are just a few examples of the many Git hosting platforms available to users. Each platform has its own unique features and benefits, so it’s important to evaluate them based on your specific needs and preferences.
What are the advanced topics on Git?
Git is a powerful tool that goes beyond the basics of version control. In this section, we will cover some of the more advanced topics.
- Rebasing: rebasing is a technique for integrating changes from one branch into another. Instead of merging the changes, rebasing applies them directly to the target branch. This makes the branching process more linear and clear.
- Submodules: Submodules allow you to include a repository as a subdirectory within another repository. This is useful if you want to include code from another project in your own project. Working with submodules can be a bit complicated, but they can be a powerful tool if used correctly.
- Git Hooks: Hooks are scripts that are automatically executed at certain points in the workflow. For example, you can use a pre-commit hook to run tests before committing your code. These scripts can be used to enforce coding standards, automate repetitive tasks, and more.
- Git bisect: This command helps you find the commit that introduced a bug. You start by identifying a “good” commit (a commit where the code works) and a “bad” commit (a commit where the code is buggy). Git bisect then checks the intermediate commits and prompts you to test each one until it finds the commit that introduced the error.
- Git stash: This allows you to temporarily store changes that you don’t want to commit yet. This can be useful if you need to switch to another branch or pull changes from a remote repository. Saving changes allows you to keep your working directory clean without losing changes.
These are just a few examples of the advanced topics you can explore in Git. Once you master these techniques and tools, you can become an efficient and effective user.
This is what you should take with you
- Git is a decentralized version control with the help of which complex programming projects can be executed in teamwork.
- With the help of Git, several people can work on the same project and make changes and still ensure that the individual functions later work as a whole.
- The advantages of Git are that the probability of failure is very low since each member has a reasonably current state of the repository stored on their device. In addition, older version statuses can always be reverted to.
What are Classes and Objects in Python?
Mastering Python's Object-Oriented Programming: Explore Classes, Objects, and their Interactions in our Informative Article!
What is Threading and Multiprocessing in Python?
Boost your Python performance and efficiency with threading and multiprocessing techniques. Learn how to harness parallel processing power.
What is Anaconda for Python?
Learn the essentials of Anaconda in Python for efficient package management and data science workflows. Boost your productivity today!
What are Regular Expressions?
Unlock powerful text manipulation in Python with regular expressions. Master patterns, syntax, and advanced techniques for data processing.
What is Object-Oriented Programming?
Master Object-Oriented Programming concepts in Python with our beginner's guide. Learn to create reusable code and optimize your coding skills.
What is Plotly?
Learn how to create interactive visualizations and dashboards with Plotly, a Python data visualization library.
Other Articles on the Topic of Git
w3schools provides detailed explanations of useful Git commands.