Python operators are special types of functions that perform certain, mostly mathematical, operations in the Python programming language.
What are Operators?
In Python, there are the so-called operators, which, like a function, execute fixed-defined actions. However, a function does not have to be defined in a conventional way, but much shorter operators can be used. Python operators are already installed in the basic version of Python and do not have to be added by importing an additional module.
More generally, a Python operator consists of the left side, the operator, and the right side. The operator determines what happens to the right and left sides. Depending on the source, this is also referred to as the operands. We will use this term in this article.
There are countless operators in Python which we will discuss further in the following chapters. One of them is the mathematical difference, which can be called using the character “-“.
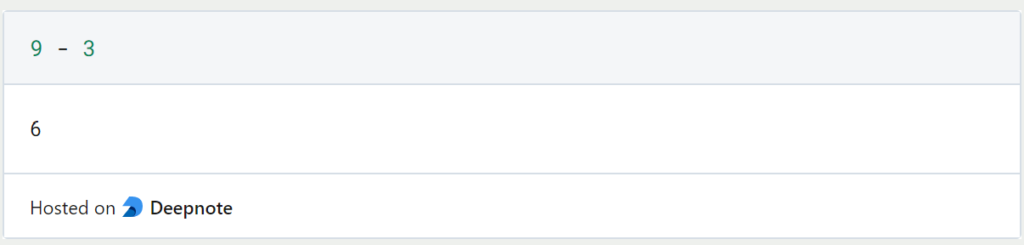
In our example, the minus sign is the operator. The two operands are the numbers nine and three. Finally, the number six is the result of the operation.
What are the types of Python Operators?
Python distinguishes between different types of operators, which we will explain in more detail in the following chapters.
Comparison Operators
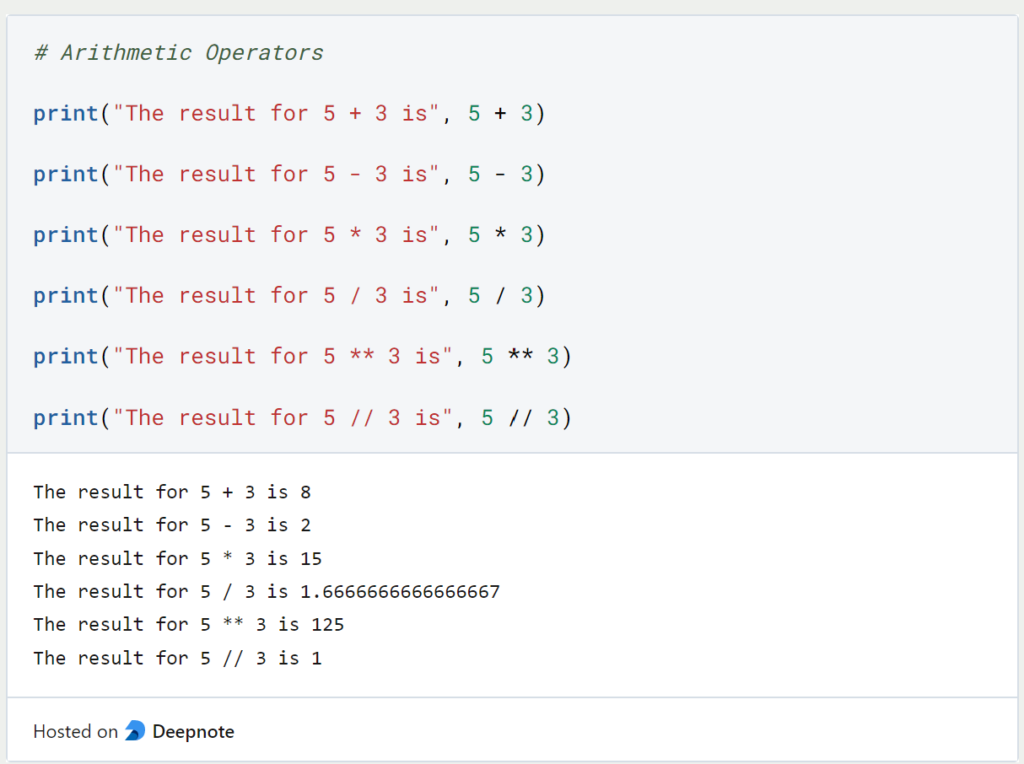
The comparison operators can compare two operands with each other. They always return a Boolean value (True or False) as the result.
| Operator | Short | Meaning | Example |
| > | greater | Checks if the left operand is greater than the right operand | 5 > 3 |
| < | smaller | Checks if the left operand is smaller than the right operand | 5 < 3 |
| == | equal | Checks if the two operands are identical | 5 == 3 |
| != | unequal | Checks if the two operands are not identical | 5 != 3 |
| >= | greater or equal | Checks if the left operand is greater than or equal to the right operand | 5 >= 3 |
| <= | smaller or equal | Checks if the left operand is less than or equal to the right operand | 5 <= 3 |
Arithmetic / Mathematical Operators
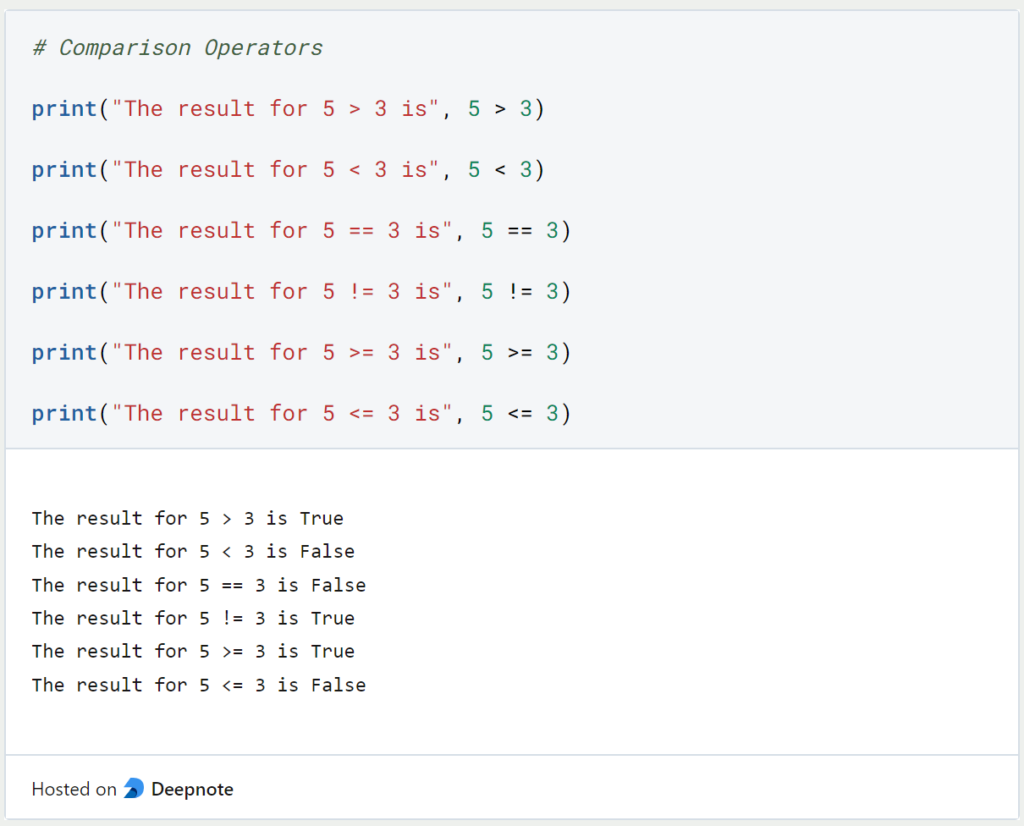
The mathematical or arithmetic operators implement basic mathematical functions in Python. For this, the basic calculation types, such as sum, difference, multiplication, etc. are covered.
| Operator | Short | Meaning | Example |
| + | Sum | Adds the left and right operands together | 5 + 3 |
| – | Difference | Subtracts the right operand from the left operand | 5 – 3 |
| * | Multiplication | Multiplies the right operand with the left operand | 5 * 3 |
| / | Division | Divides the left operand by the right operand | 5 / 3 |
| ** | Exponentiation | Forms the exponent with the left operand as the base and the right operand as the superscript | 5**3 |
| // | Division with remainder | Divides the left operand by the right operand using integer division | 5 // 3 |
Logical Operators
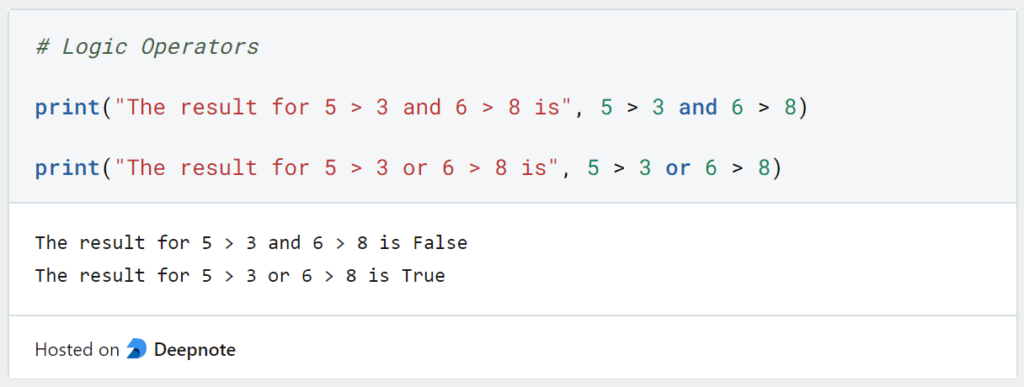
The logical operators are also from mathematics and enable the connection of conditions with the help of the logical And and Or. Two statements linked with “or” are true exactly when one of the two statements is true. Two statements linked with “and” are true exactly when both statements are true.
| Operator | Short | Meaning | Example |
| and | Logical And | Returns True if all conditions are True | 5 > 3 and 6 > 8 |
| or | Logical Or | Returns True if one of the conditions is True | 5 > 3 or 6 > 8 |
Identity Operator
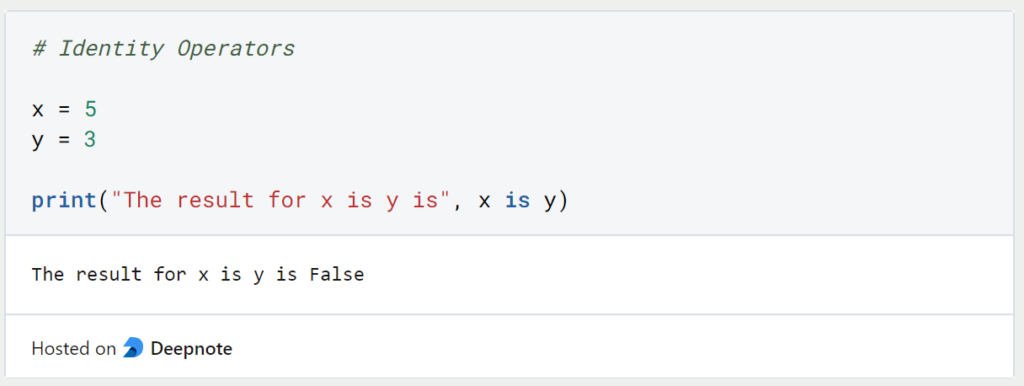
The Python operator “is” is used to check whether two variables have the same value assigned to them. The operator then returns True or False accordingly. This can also be used to check dynamically in a script whether the variables are identical.
Subset Operator
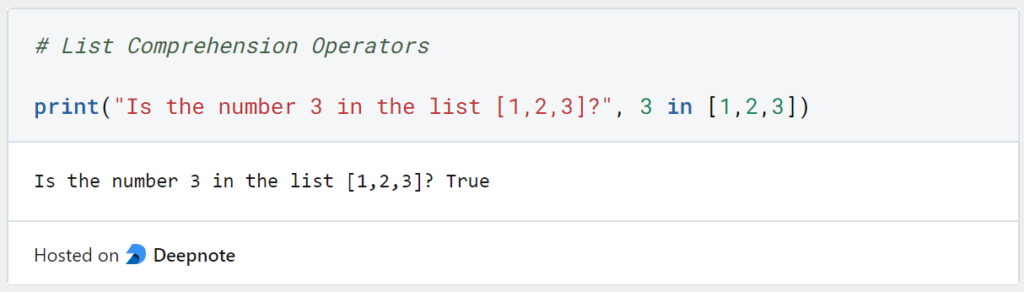
The subset operators can be used to check whether one or more elements are present in a set, such as a Python List.
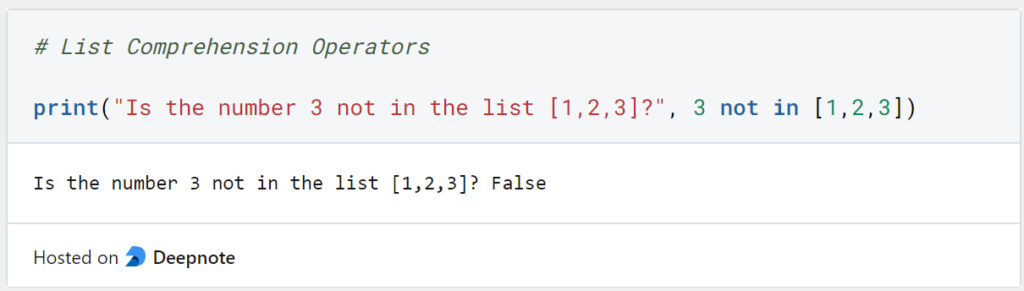
The negation can be used to check the opposite, i.e. whether the element is not part of the set.
Assignment Operators
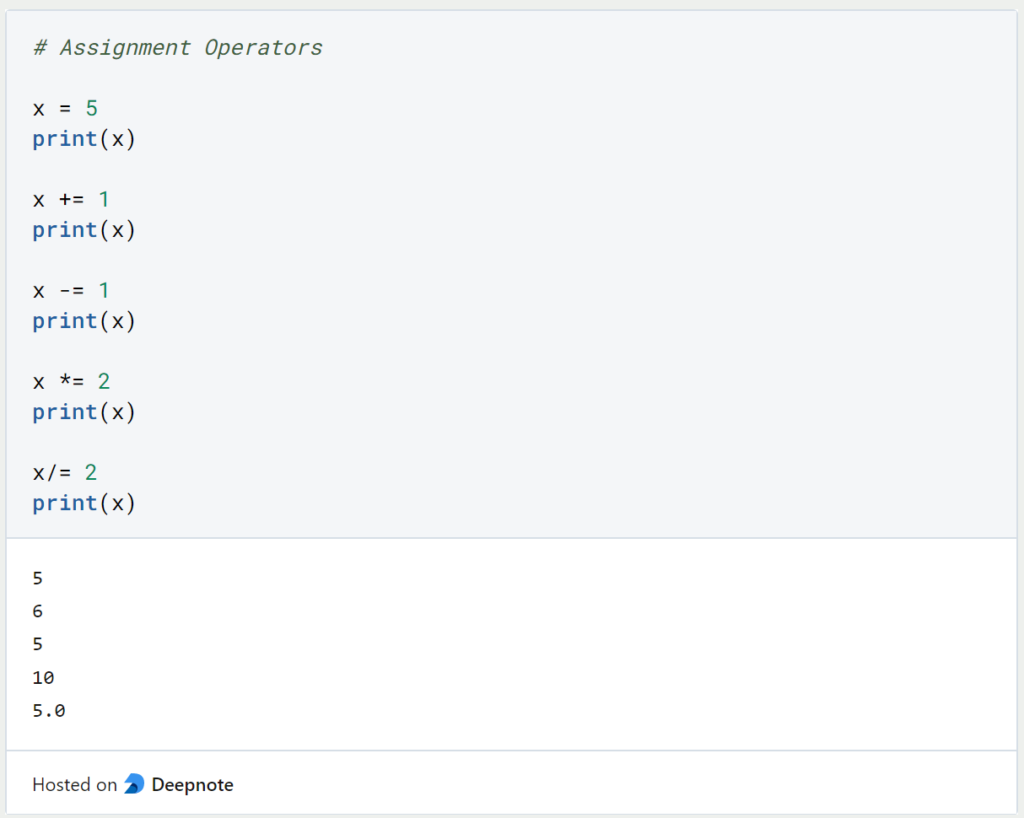
We already know the most basic assignment operator from the definition of a variable. With the help of the “=” we can assign a value to a variable. In addition, there are other assignment operators with the help of which, for example, sums or products can be written in a shortened form.
| Operator | Meaning | Example |
| = | Assigns a value to a variable | x = 5 |
| += 1 | Increases the value of a variable by 1 | x += 1 |
| -= 1 | Decreases the value of a variable by 1 | x -= 1 |
| *= 2 | Multiplies the value of a variable with 2 | x *= 2 |
| /= 2 | Divides the value of a variable by 2 | x /= 2 |
This is what you should take with you
- Python operators are special types of functions that mostly perform mathematical functions.
- Python operators allow quick invocation without the need to define a new function.
- There are different types, such as logical operators or assignment operators.
What is Jenkins?
Mastering Jenkins: Streamline DevOps with Powerful Automation. Learn CI/CD Concepts & Boost Software Delivery.
What are Conditional Statements in Python?
Learn how to use conditional statements in Python. Understand if-else, nested if, and elif statements for efficient programming.
What is XOR?
Explore XOR: The Exclusive OR operator's role in logic, encryption, math, AI, and technology.
How can you do Python Exception Handling?
Unlocking the Art of Python Exception Handling: Best Practices, Tips, and Key Differences Between Python 2 and Python 3.
What are Python Modules?
Explore Python modules: understand their role, enhance functionality, and streamline coding in diverse applications.
What are Python Comparison Operators?
Master Python comparison operators for precise logic and decision-making in programming.
Other Articles on the Topic of Python Operators
- w3schools offer a detailed tutorial on Python operators.

Niklas Lang
I have been working as a machine learning engineer and software developer since 2020 and am passionate about the world of data, algorithms and software development. In addition to my work in the field, I teach at several German universities, including the IU International University of Applied Sciences and the Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, in the fields of data science, mathematics and business analytics.
My goal is to present complex topics such as statistics and machine learning in a way that makes them not only understandable, but also exciting and tangible. I combine practical experience from industry with sound theoretical foundations to prepare my students in the best possible way for the challenges of the data world.





