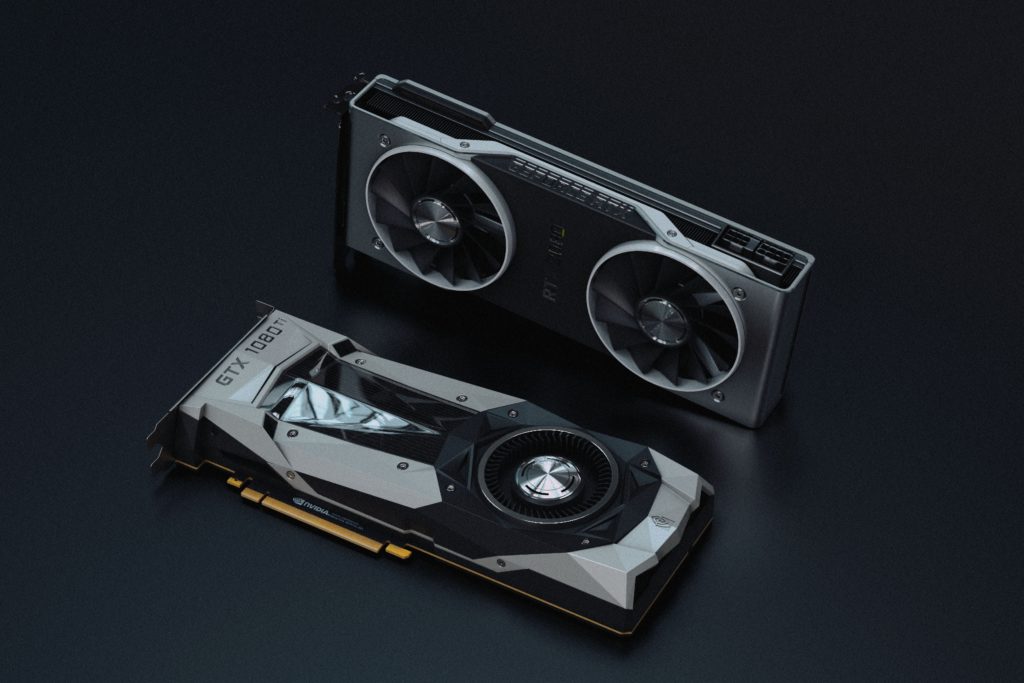
The graphics card, also known as the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), is responsible for calculating images in a computer, which can then be displayed on a monitor. It represents the interface between the processor’s calculations and the monitor. However, the development of graphics cards is now so far advanced that, in addition to this function, they can also support and relieve the CPU during calculations.
How does the Graphics Card work?
The computer’s processor calculates what data a certain program wants to display on the screen and outputs it as so-called image data. This mostly numerical, data is then converted by the GPU so that it can be displayed on a monitor or other device.
Many laptops and computers contain graphics cards that are already mounted on the circuit board, i.e. the mainboard. Such integrated graphics cards (IGP) do not have their memory and also access the computer’s main memory. Due to the IGP’s lack of a memory component, the size is very small and can thus be used primarily for small devices, such as tablets or notebooks. However, this design is accompanied by a low clock rate and lower performance due to the shared working memory. Thus, IGPs are mainly used in devices that are mainly intended for office applications or browsing.
The opposite of this is the dedicated graphics card, which has its memory, the so-called VRAM. However, this also increases the size and requires cooling. Therefore, dedicated GPUs are separate components that are usually connected to the motherboard via the PCI interface. Due to their memory, they are significantly more powerful and are used in devices that are used for gaming or machine learning purposes, for example. The majority of the remaining article will mainly deal with dedicated graphics cards since there are now significantly more use cases that require such a GPU.
What are the Components of a Graphics Card?
In many cases, a GPU consists of the following components:
- Fan
- Cooling Device
- Graphics processor
- Memory
- Memory interface
- Board
- Connectors for graphics outputs (VGA, Displayport, etc.)
We will now go into detail about the most important components:
Graphics Chip
The graphics chip does the actual work of the graphics card and is the brain of the system. This is where the calculations of the images are made. The other components are largely occupied with equipping the graphics chip as much as possible so that it can work at full performance and does not have to wait for the memory, for example.
Graphics Memory
The graphics memory stores all the data needed to calculate image and video files. As already mentioned, the separate memory can be used to bypass access to the computer’s main memory and thus maintain the computer’s performance.
The memory size and the connection play a decisive role in the selection so that the graphics memory does not suffer from performance losses. Overall, there is no component within the graphics card where compromises should be made anyway, otherwise, the performance of the entire system will always suffer, no matter how powerful the rest of the components are.
Memory Interface
The memory interface determines the bandwidth with which the data can be accessed. The higher the bandwidth, the more data can be transferred in a short time, which is especially important for computer games with high frame rates, i.e. many changing images.
Higher bit rates of the memory interface can generally be equated with more performance. You can think of the memory interface as the “storage” of the graphics chip. The higher the bit rate, the larger the usable storage area. In turn, with more area, the data can be placed more clearly and can thus be used again more quickly. In many graphics cards, the memory interface is the bottleneck that prevents more system performance.
Cooling Device
A powerful GPU is only performant in combination with a sufficient cooling unit. Otherwise, the GPU can quickly overheat and the performance has to be throttled to prevent damage. However, GPUs should generally be able to withstand temperatures of 100 °C for a short time.
Depending on the GPU, active or passive cooling is used. Active cooling is still known from older devices, which emit an unmistakable fan noise when the performance increases. Active cooling is characterized by actively trying to transport the heat away from the chip. In most cases, a fan is still used, which runs at a higher or lower speed depending on the heat pattern. However, this has the disadvantage that it comes to the already described sound pattern during heavy use.
In passive cooling, on the other hand, the heat is transported away from the chip via a cooling medium, such as a liquid. The surface of the cooling device is designed very large to be able to absorb a lot of heat under load. This means that there is no additional noise even at high performance.
For which Applications do you need good Graphics Cards?
As we have already seen, all programs that have a visual output need a graphics card to be able to create the corresponding images and videos. However, integrated graphics cards are perfectly sufficient for many programs.
Beyond that, some special applications require significantly more graphics performance and therefore cannot do without a powerful, usually dedicated graphics card. These include, among others:
- Gaming: To enable fast image changes in action-packed computer games, a powerful graphics card must be able to process large amounts of data within a short time.
- 3D Modeling: When new cars, machines, or other parts are designed and planned, 3D models are created to visualize components. If the component is to be viewed from different angles, the graphics card must calculate the new views within fractions of a second, otherwise, the image may judder.
- Image Processing and Video Editing: Nowadays, images and videos are increasingly high-resolution, i.e. they contain more pixels than before. To be able to process all these pixels quickly, more performance is also required from the GPU.
- Machine Learning: The topic of Machine Learning does not fit so well into the previous list, since no high-resolution or quickly changing image sequences are needed here. However, powerful graphics cards are also very important for machine learning, since so-called tensors are used for work and calculations. These are very similar to the numerical representation of images. As a result, a GPU can calculate machine learning models much faster than conventional processors.
How to find the perfect Graphics Card?
First, it’s best to determine the budget you’re willing to spend on a new GPU. This market is like many others, and often you can only get more performance at a higher price. Currently, you can’t get good dedicated graphics cards for less than 180 €. All models below are in most cases not more powerful than the already installed GPUs.
The mid-range models range from about 300 to 550 €, which should be sufficient for current games. The absolute top performance can only be achieved with models above 550€. The leading graphics card in many rankings, NVIDIA RTX 3090 Ti with 24 GB VRAM, is even around 1,500€.
As already mentioned, the GPU is embedded in a system of components and can only deliver the fastest performance if the interaction with the rest of the PC runs smoothly. Therefore, a very good graphics card alone is not enough, it should be paired with new components, like a powerful processor. Especially the new and usually expensive GPUs should also be surrounded by up-to-date components to exploit their full potential.
Finally, compatibility with the previous computer must be ensured, otherwise, the graphics card would not be usable. To be on the safe side, you can use one of many free PC configurators and check the compatibility. To do this, you simply select the components you already have, such as CPU, RAM, mainboard, etc., and then select the graphics card you want. This will give a clear answer to whether the components fit together or not. Additionally, not only the compatibility with the other components counts but also sufficient installation space for the new GPU.
What is the difference between GPU and CPU?
Both a graphics card and a processor contribute to the performance of a computer. However, they fulfill different tasks and functions. You should therefore be aware of the differences before purchasing to be able to assess which of the components you should place more emphasis on when buying.
A CPU is an all-purpose weapon that is used for a variety of tasks, such as handling system processes or managing input and output, for example via the keyboard. The processor can have different cores, usually between two and 16. Tasks can be executed in parallel on these processors, but the CPU concentrates on executing one task as quickly as possible so that it can continue with the next.
A graphics card (GPU), on the other hand, is a specialized processor for processing graphics and image processing tasks. It is optimized for parallel processing of tasks and can process many applications simultaneously. The number of cores in a graphics card is also significantly higher than in a CPU and can range from several hundred to several thousand. These are used to perform calculations quickly and efficiently. Since the processing of images works in vectors, GPUs can also be used for machine learning tasks that involve so-called tensors.
The main differences between a GPU and a CPU are:
- Architecture: The graphics card is designed for parallel processing and has a very large number of cores for this purpose. The CPU, on the other hand, prefers sequential processing of tasks and therefore executes them one after the other. Only a small number of cores are required for this.
- How it works: The general processor, i.e. the CPU, is designed for simple and everyday tasks that arise during almost every interaction with the computer. The graphics card, on the other hand, is used for more complex calculations, such as rendering 3D graphics or machine learning.
- Performance: The graphics processor can offer significant performance advantages over the CPU for computationally intensive tasks, as these are performed in parallel. Therefore, when programming, care should be taken to select the right processor for the respective tasks to be able to use the full performance of the device.
In conclusion, it can be said that GPUs and CPUs differ primarily in their architecture and functionality. While a CPU is used for general tasks, the graphics card is ideal for complex calculations, such as in image processing.
This is what you should take with you
- The graphics card, also called the Graphics Processing Unit (GPU), is responsible for calculating images in a computer, which can then be displayed on a monitor.
- The graphics card can either be installed on the motherboard of the computer, i.e. integrated, or connected as an external component, i.e. dedicated.
- It consists of several important components, such as the graphics chip, the graphics memory, the memory interface, and the cooling. Only when these components are sufficiently coordinated can the full performance of the graphics card be accessed.
- Powerful graphics cards are especially important for gaming, image editing, and machine learning.
- When selecting a new graphics card, compatibility with other components should be taken into account.
What is Collaborative Filtering?
Unlock personalized recommendations with collaborative filtering. Discover how this powerful technique enhances user experiences. Learn more!
What is Quantum Computing?
Dive into the quantum revolution with our article of quantum computing. Uncover the future of computation and its transformative potential.
What is Anomaly Detection?
Discover effective anomaly detection techniques in data analysis. Detect outliers and unusual patterns for improved insights. Learn more now!
What is the T5-Model?
Unlocking Text Generation: Discover the Power of T5 Model for Advanced NLP Tasks - Learn Implementation and Benefits.
What is MLOps?
Discover the world of MLOps and learn how it revolutionizes machine learning deployments. Explore key concepts and best practices.
Other Articles on the Topic of Graphics Card

Niklas Lang
I have been working as a machine learning engineer and software developer since 2020 and am passionate about the world of data, algorithms and software development. In addition to my work in the field, I teach at several German universities, including the IU International University of Applied Sciences and the Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, in the fields of data science, mathematics and business analytics.
My goal is to present complex topics such as statistics and machine learning in a way that makes them not only understandable, but also exciting and tangible. I combine practical experience from industry with sound theoretical foundations to prepare my students in the best possible way for the challenges of the data world.