The Python tuple is used to store multiple values in a variable. It is one of four data structures that are pre-installed in Python. In addition to the tuple, these also include the dictionary, the set, and the list.
The tuple is ordered and cannot be changed. On the one hand, this means that the elements have a specific and constant order. Due to the fixed order, the tuple also allows duplicates. On the other hand, the tuple cannot be changed after it has been defined. Thus, no elements can be deleted or added.
How to create a Tuple?
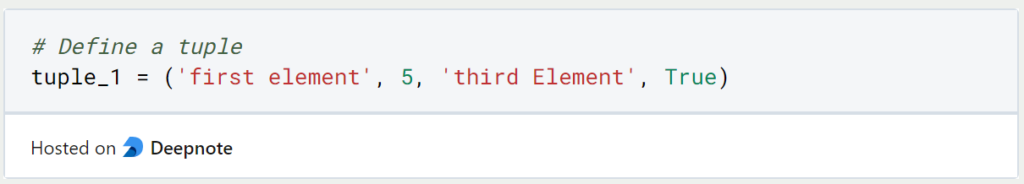
We can create a Python tuple by defining the elements in round brackets and separating them with commas. Elements with different data types can be stored in a tuple without any problems.
There is also the possibility to define a Python tuple without round brackets, simply by enumerating the elements separated by commas. However, this notation is rather rare and ambiguous, which is why it often leads to confusion as well. Therefore, tuples are always explicitly defined with round brackets in this article.

How to query elements?
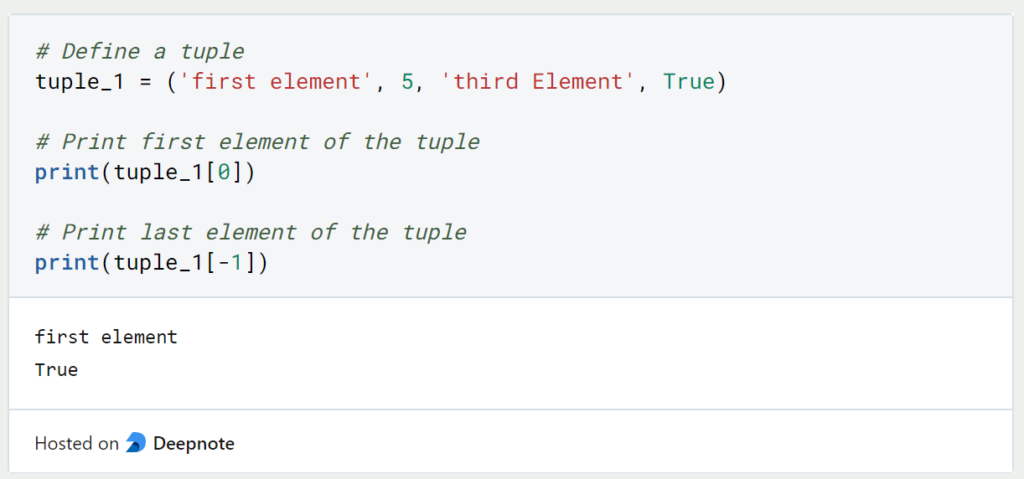
Due to the order of a Tuple, we can resort to indices to retrieve individual elements from the tuple. It should be noted that the counting of elements starts at 0. If we want to retrieve a value from the end, on the other hand, we start counting at 1.
If we don’t know the index of a certain element yet, we can ask for it with the method “index”. Since the order within the Python Tuple does not change, this value also remains.

How to change elements?
As we have already learned, Tuples are actually immutable. That is, once we have defined a Tuple, it is no longer possible to add or delete elements.
To be able to change Tuples anyway, we use a little trick. We first convert the Tuple into a Python list. Since this is changeable, we can simply add or remove elements here. Then we convert the list back to a Tuple. This way we have indirectly changed the elements of the Python Tuple.

How can multiple tuples be merged?
If we want to merge two or more Tuples, we can simply use the “+” operator. The first named Tuple is accordingly in the order before the second named Tuple.

How to count the elements in a Tuple?
The “count” function can be used to count the occurrences of a specific element in a Python Tuple:

Which Python collections are available?
In Python, there are a total of four data types that are stored by default:
- The list is an ordered collection of elements, which is changeable and can also contain duplicate elements.
- The tuple is in effect a list, with the difference that it is no longer changeable. So no elements can be added or removed afterward.
- The set does not allow duplicate entries. At the same time, the arrangement of the elements within the set is variable. The set itself can be changed, but the individual elements cannot be changed afterward.
- Since Python version 3.7, a dictionary is an ordered collection of key-value pairs that can be changed. In the earlier versions, the dictionary is unordered.
This is what you should take with you
- The Python Tuple is one of four pre-installed data structures in Python.
- It is used to store multiple values in a single variable.
- The Tuple cannot be modified after it has been created. It is also ordered, which means that the values have a predefined order.
Thanks to Deepnote for sponsoring this article! Deepnote offers me the possibility to embed Python code easily and quickly on this website and also to host the related notebooks in the cloud.
Python Programming Basics: Learn it from scratch!
Master Python Programming Basics with our guide. Learn more about syntax, data types, control structures, and more. Start coding today!
What are Python Variables?
Dive into Python Variables: Explore data storage, dynamic typing, scoping, and best practices for efficient and readable code.
What is Jenkins?
Mastering Jenkins: Streamline DevOps with Powerful Automation. Learn CI/CD Concepts & Boost Software Delivery.
What are Conditional Statements in Python?
Learn how to use conditional statements in Python. Understand if-else, nested if, and elif statements for efficient programming.
What is XOR?
Explore XOR: The Exclusive OR operator's role in logic, encryption, math, AI, and technology.
How can you do Python Exception Handling?
Unlocking the Art of Python Exception Handling: Best Practices, Tips, and Key Differences Between Python 2 and Python 3.
Other Articles on the Topic of Python Tuples
- w3schools offers detailed examples of Python Tuples with the possibility to execute code snippets directly online.

Niklas Lang
I have been working as a machine learning engineer and software developer since 2020 and am passionate about the world of data, algorithms and software development. In addition to my work in the field, I teach at several German universities, including the IU International University of Applied Sciences and the Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, in the fields of data science, mathematics and business analytics.
My goal is to present complex topics such as statistics and machine learning in a way that makes them not only understandable, but also exciting and tangible. I combine practical experience from industry with sound theoretical foundations to prepare my students in the best possible way for the challenges of the data world.





