A business analyst monitors various business processes and checks whether these processes are running satisfactorily or whether there is potential for improvement. A business analyst is first employed independently of a specific discipline or department and acts as a link between different departments and stakeholders.
What are the tasks?
As an analyst, you are employed in various areas of a company. The aim is to identify problems in business processes, make them measurable and evaluable, and use the data to develop new concepts and improvements.
You have to communicate with a wide variety of stakeholders, such as different departments, the management, or IT. As the link between technology and sales, you try to record the requirements and convert them into a technical concept. The cost-effectiveness of the solution is of immense importance.
The main tasks are:
- Gathering and recording business requirements
- Conversion of requirements into technically feasible concepts
- Analysis and preparation of processes
- Participation in project teams consisting of representatives from business and IT
- Management of the introduction and implementation of the proposed concepts
- Mediation between technical and business departments
What industries are looking for business analysts?
Business analysts are actually needed in all industries and are used wherever there is a need to mediate between the IT department and the business. Analysts are used primarily in the logistics, finance, and insurance industries.
In addition, many other companies have recognized the power of their data and are trying to exploit it to the maximum. Thus, there are also opportunities in all areas where organizations are sitting on large amounts of data. This includes companies that operate a production line and therefore have a large amount of sensor or quality data. In the same way, however, large quantities of information can also be available in retail or e-commerce, which are to be evaluated in a targeted and goal-oriented manner.
What skills should you bring?
Several types of skills are needed to be a Business Analyst.
A central task is the development of new solutions based on data. This requires certain creativity and an understanding of business processes. In order for a solution to be found at all, the requirements must of course first be correctly recorded. Subsequently, technical skills in business intelligence tools, such as Power BI or Tableau, as well as basic knowledge of programming languages, such as Python, are required in order to be able to carry out a well-founded data analysis.
Finally, the results must be communicated in an understandable way to an audience outside the field, so good presentation skills and the creation of easy-to-understand visualizations are indispensable for the job as a business analyst.
In addition, classic soft skills such as the ability to work in a team, empathy, stress resistance, etc. are of course also an advantage for the job as an analyst. A basic understanding of economics is useful in order to be able to directly check the presented findings and solutions for their feasibility and economic viability.
What tools and methods does a business analyst use?
Business Analysts use a variety of tools and technologies to collect, analyze, and interpret data. Some of the commonly used tools and technologies include:
- Spreadsheets: Business Analysts use spreadsheets such as Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or Apple Numbers to store and analyze data. They may use formulas, tables, and charts to analyze data and visualize trends.
- Business intelligence (BI) software: BI software such as Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView enable business analysts to create dashboards and reports, analyze data, and make data-driven decisions.
- Statistical analysis software: Business analysts use statistical analysis software such as R or SAS to analyze large data sets and perform advanced statistical analysis. These tools help with data modeling, predictive analytics, and machine learning.
- Data visualization tools: Tools like D3.js, Plotly, and ggplot2 are used by business analysts to create visual representations of data. These tools help in identifying patterns, trends, and outliers.
- Project management software: Business Analysts use project management tools such as Asana, Trello, or Jira to manage their work, track progress, and collaborate with team members.
- Data integration and ETL tools: Enterprise analysts use data integration and ETL (extract, transform, load) tools such as Talend, Informatica, or Apache NiFi to integrate data from multiple sources, transform the data into the desired format and load it into a database or data warehouse.
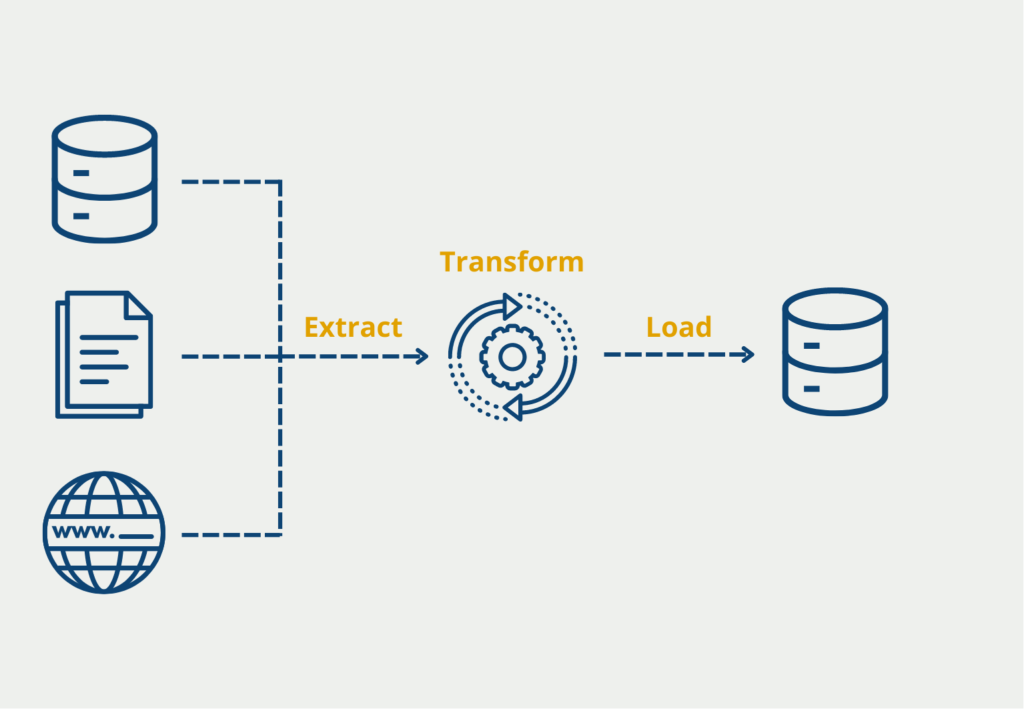
- SQL and relational databases: Business analysts use SQL (Structured Query Language) to retrieve data from relational databases such as MySQL, Oracle, or SQL Server. They use SQL to write queries to extract data, perform data analysis, and create reports.
- Machine learning platforms: Machine learning platforms such as TensorFlow, Keras, or PyTorch are used by enterprise analysts to build and deploy machine learning models. These tools help with predictive modeling, natural language processing, and image recognition.
Overall, business analysts use a variety of tools and technologies to collect, analyze, and interpret data to make business decisions and improve business performance.
What kind of education is needed?
If you take a closer look at various job offers, you will notice that companies do not demand a specific course of study for prospective business analysts. There are various fields of study that are seen as good prerequisites for a career as an analyst. These include, for example, economic courses of study, such as economics or business administration, as well as technical courses of study, such as computer science, mathematics, or physics. Of course, mixtures of both disciplines, i.e. business informatics or business mathematics, are also ideally suited for a career as a business analyst.
Depending on the industry and company, IT-related training with several years of professional experience is also accepted for these positions. This varies depending on the job and must be differentiated in each individual case.
What are the benefits of having a business analyst on a team?
Having a business analyst on a team or project can bring several benefits, including:
- Better decision-making: Business analysts can provide valuable insights into market trends, customer needs, and industry best practices that can inform strategic decision-making.
- Increased efficiency: By analyzing business processes, identifying opportunities for improvement, and implementing solutions, business analysts can help streamline operations and reduce costs.
- Better communication: These employees can act as a liaison between different departments, facilitating communication and collaboration between teams.
- Better risk management: By conducting risk assessments and developing mitigation strategies, business analysts can help companies avoid potential problems and minimize the impact of issues that do arise.
- Improved customer satisfaction: By analyzing customer data and feedback, business analysts can help companies better understand the needs and preferences of their customers, leading to the development of more effective products and services.
Overall, having a business analyst on a team or project can help companies make better decisions, operate more efficiently, and ultimately achieve their business goals.
What are the differences between a Business Analyst and a Data Scientist?
While there is some overlap between the roles of a Business Analyst and a Data Scientist, there are also some important differences:
- Focus: Business Analysts typically focus on the business side of things, such as identifying business problems and proposing solutions. Data Scientists, on the other hand, tend to focus on the technical side of things, such as collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data.
- Tools and Techniques: Business Analysts typically use tools such as spreadsheets, flowcharts, and process maps to analyze data and identify patterns. Data Scientists, on the other hand, typically use more advanced tools and techniques, such as machine learning algorithms and statistical models.
- Data Sources: Business Analysts typically work with structured data, such as sales figures or customer demographic data. Data Scientists, on the other hand, often work with unstructured data, such as text or images.
- Scope: Business Analysts typically focus on a specific business unit or department, while Data Scientists often work on larger projects that span multiple units and departments.
Overall, while there is some overlap between the roles of a business analyst and a data scientist, they tend to have different focuses, tools and techniques, data sources, and areas of work.
This is what you should take with you
- Business analysts act as an interface between the business department and IT.
- They try to analyze existing processes, present them in a comprehensible way, and at the same time make suggestions for improvement.
- There are currently job openings in virtually all industries. However, business analysts are of immense importance, especially in the areas of logistics and finance.
What is Collaborative Filtering?
Unlock personalized recommendations with collaborative filtering. Discover how this powerful technique enhances user experiences. Learn more!
What is Quantum Computing?
Dive into the quantum revolution with our article of quantum computing. Uncover the future of computation and its transformative potential.
What is Anomaly Detection?
Discover effective anomaly detection techniques in data analysis. Detect outliers and unusual patterns for improved insights. Learn more now!
What is the T5-Model?
Unlocking Text Generation: Discover the Power of T5 Model for Advanced NLP Tasks - Learn Implementation and Benefits.
What is MLOps?
Discover the world of MLOps and learn how it revolutionizes machine learning deployments. Explore key concepts and best practices.
Other Articles on the Topic of Business Analysts
- Here you can find current job offers as Business Analyst in your region.

Niklas Lang
I have been working as a machine learning engineer and software developer since 2020 and am passionate about the world of data, algorithms and software development. In addition to my work in the field, I teach at several German universities, including the IU International University of Applied Sciences and the Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, in the fields of data science, mathematics and business analytics.
My goal is to present complex topics such as statistics and machine learning in a way that makes them not only understandable, but also exciting and tangible. I combine practical experience from industry with sound theoretical foundations to prepare my students in the best possible way for the challenges of the data world.