Blockchain-based AI is a rapidly evolving field that aims to leverage the power of blockchain technology to enhance the capabilities of artificial intelligence. By combining the decentralized, secure, and transparent nature of blockchain with the intelligence and efficiency of AI, this field is poised to revolutionize a variety of industries and applications. From enhancing supply chain management to improving cybersecurity and data privacy, the potential uses of blockchain-based AI are vast and varied.
In this article, we will explore the key concepts, benefits, and challenges associated with blockchain-based AI, as well as some real-world examples of its applications.
What is blockchain technology and its key features?
Blockchain is a revolutionary technology that has been gaining significant attention in recent years. At its core, it is a distributed and decentralized system for recording transactions and data in a secure and transparent manner. Unlike traditional centralized systems, where a single authority has control over the data, blockchain operates as a network of computers, known as nodes, that work together to validate and store information.
The fundamental concept behind blockchain is its ability to create a tamper-resistant and immutable ledger. Each transaction or piece of data is grouped into a block, which is then linked to the previous block, forming a chain. Once a block is added to the chain, it becomes virtually impossible to alter or delete the information within it. This feature ensures the integrity and authenticity of the data, making it ideal for applications where trust and transparency are essential.
One of the key features that make blockchain so unique is its decentralized nature. There is no central authority or intermediary that controls the network. Instead, all participants in the blockchain network have access to the same information, and any changes to the data must be agreed upon by a consensus mechanism. The main features of blockchain technology are:
- Decentralization: A blockchain is a decentralized database that is managed by a network of computers rather than a single entity. This means that no single party has control over the data on the blockchain.
- Immutability: Once a transaction is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be modified or deleted. This ensures the integrity of the data on the blockchain.
- Security: The security of a blockchain is ensured through the use of cryptography. Each block in the chain is secured through a cryptographic hash function, which makes it nearly impossible to tamper with the data.
- Transparency: The data on the blockchain is visible to all participants on the network, providing a high degree of transparency.
The key features of blockchain technology make it an ideal platform for applications that require secure, transparent, and decentralized systems. One such application is Artificial Intelligence (AI), where blockchain technology can be used to enhance the security, privacy, and efficiency of AI systems.
The security of blockchain is further enhanced through cryptography. Each transaction is encrypted and linked to the previous one using complex mathematical algorithms. This ensures that the data is protected from unauthorized access and manipulation.
Blockchain technology has far-reaching implications beyond its use in cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. It has the potential to revolutionize various industries, including finance, supply chain management, healthcare, real estate, and more. By providing a secure, transparent, and efficient way to record and verify transactions, blockchain has the power to transform how we conduct business and interact with each other.
In summary, blockchain is a game-changing technology that offers a new paradigm for data management and security. Its decentralized, transparent, and tamper-resistant nature has the potential to disrupt numerous industries and create new opportunities for innovation. As blockchain continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play a crucial role in shaping the future of technology and society as a whole.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence, often abbreviated as AI, is a fascinating field of computer science that aims to create intelligent machines that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks can include learning from experience, recognizing patterns, understanding natural language, making decisions, and even solving complex problems.
At its core, AI seeks to mimic human cognitive abilities in machines by using algorithms, data, and computational power. The goal is to enable machines to process information, reason, and learn from data in a way that allows them to make autonomous decisions and adapt to new situations without explicit programming.
There are two main types of AI: Narrow AI and General AI. Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed to perform specific tasks, such as voice assistants like Siri or recommendation systems on streaming platforms. These systems excel in their particular domains but lack the ability to generalize their knowledge beyond their predefined tasks.
On the other hand, General AI, also known as Strong AI or AGI (Artificial General Intelligence), is a theoretical concept where machines possess the same level of intelligence as humans. AGI would be capable of understanding and learning any intellectual task that a human can do. While we have not yet achieved AGI, it remains a long-term goal of the AI community.
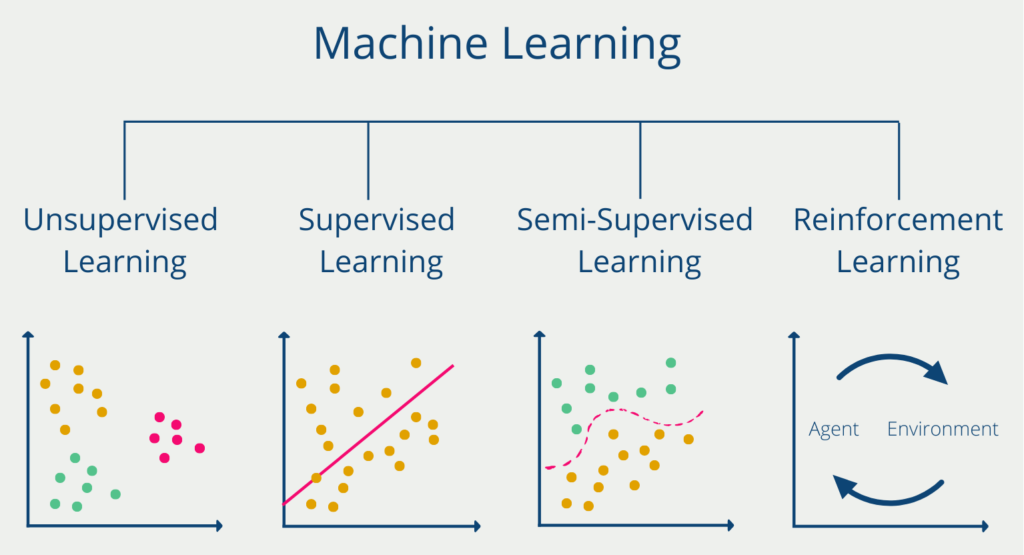
AI algorithms can be broadly classified into three categories: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model using labeled data, where the algorithm learns to map input data to the correct output. Unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data, and the algorithm tries to find patterns and structure within the data. Reinforcement learning is inspired by behavioral psychology, where an agent learns to interact with an environment and receives feedback in the form of rewards or punishments.
The applications of AI are vast and continue to grow rapidly. From virtual assistants and chatbots to autonomous vehicles, AI is shaping various industries, including healthcare, finance, education, and manufacturing. It’s also used in natural language processing, computer vision, robotics, and more.
While AI offers immense opportunities and benefits, it also raises ethical and societal concerns. As AI becomes more pervasive, discussions around privacy, bias in algorithms, and the impact on the job market are crucial to address.
In conclusion, artificial intelligence is a captivating field that holds the promise of transforming the world by creating intelligent machines. With its diverse applications and ongoing advancements, AI will undoubtedly play a significant role in shaping our future. For beginners, exploring AI opens doors to a world of innovation, problem-solving, and opportunities to contribute to the exciting developments in this field.
What are the benefits of combining blockchain and AI?
Combining blockchain and AI can provide several benefits, such as:
- Transparency: Blockchain-based AI systems provide transparency by enabling all parties to access the data in the network and verifying the authenticity of the data.
- Security: Blockchain technology provides a secure way to store and transmit data by using cryptographic techniques. The decentralized nature of the blockchain ensures that the data cannot be easily tampered with, ensuring the security and integrity of the data.
- Privacy: With blockchain-based AI, users can maintain control of their personal data. The decentralized nature of the blockchain means that personal data can be kept private and secure, with users controlling how their data is shared.
- Increased efficiency: By combining blockchain and AI, it is possible to create autonomous systems that can perform tasks automatically and efficiently. This can lead to cost savings and increased productivity.
- Decentralization: Blockchain-based AI systems are decentralized, meaning that there is no central authority controlling the network. This can provide more freedom and flexibility for users.
- Trust: Blockchain technology is based on trust, and AI can help to improve the trustworthiness of the blockchain by providing greater accuracy and reducing the potential for errors.
Overall, the combination of blockchain and AI has the potential to revolutionize many industries by providing greater security, transparency, efficiency, and trust.
How can Smart Contracts be used for Artificial Intelligence?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They run on blockchain technology, which ensures transparency, security, and decentralization. Initially popularized by the Ethereum blockchain, smart contracts have gained significant attention for their potential to revolutionize various industries, including AI.
- Automating Transactions: Smart contracts can be utilized to automate AI-driven transactions seamlessly. For example, in a supply chain, AI algorithms can predict inventory requirements, and smart contracts can automatically trigger purchase orders when stock levels reach a certain threshold. This streamlines the procurement process, reduces human intervention, and ensures timely responses to changing demands.
- Decentralized AI Marketplaces: Smart contracts enable the creation of decentralized AI marketplaces, where AI developers can list their algorithms, models, or services. These contracts can govern the terms of usage, licensing, and payment arrangements. Users can access AI capabilities through the marketplace, and transactions are executed automatically based on predefined conditions.
- Data Privacy and Security: AI often relies on vast amounts of data for training and inference. Smart contracts can facilitate secure data sharing and enforce privacy policies. Data owners can define access rights and consent conditions through the contract, ensuring that AI models access only the necessary data while preserving privacy.
- AI Model Governance: Smart contracts can play a role in AI model governance by establishing rules for model updates, versioning, and validation. Stakeholders can collectively decide on model improvements and upgrades through decentralized decision-making processes coded in the contracts.
- AI-Enabled Financial Services: In the financial sector, AI-powered smart contracts can enhance fraud detection, credit scoring, and risk assessment. For instance, smart contracts can automatically trigger alerts when suspicious activities are detected, ensuring quick responses and reducing potential losses.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Combining AI and smart contracts can lead to the creation of decentralized autonomous organizations. AI algorithms can optimize decision-making processes within the organization, while smart contracts facilitate transparent governance and resource allocation.
- Trust and Transparency: The immutability and transparency of blockchain-based smart contracts instill trust among parties involved in AI-driven processes. All transactional records and algorithmic decisions are recorded on the blockchain, providing an auditable trail for accountability and validation.
However, while the potential of smart contracts in automating AI processes is promising, there are challenges to address. Ensuring the accuracy and fairness of AI algorithms, handling complex real-world scenarios, and managing legal and regulatory aspects of AI-based smart contracts are among the critical considerations.
In conclusion, smart contracts offer a powerful framework to automate AI processes and transactions in a secure, transparent, and decentralized manner. As blockchain technology and AI continue to evolve, the integration of these two innovations will shape a future where intelligent automation and trust converge to transform various industries and redefine the way we interact with technology.
What are the challenges and limitations of implementing blockchain-based AI?
Implementing blockchain-based AI systems brings some challenges and limitations. Some of them are:
- Scalability: Blockchain technology is known to be slow and resource-intensive, which can affect the scalability of AI applications. The larger the blockchain network, the more computing power is needed to maintain the network and process transactions.
- Privacy and security: While blockchain technology offers an unparalleled level of security, AI models that operate on personal data raise privacy concerns. In some cases, combining AI with blockchain could lead to the exposure of sensitive data to third parties.
- Integration with existing systems: Integrating blockchain-based AI systems with existing IT infrastructure can be challenging. It may require a significant investment of time and resources to ensure that the new technology operates seamlessly with legacy systems.
- Lack of standards: Currently, there is a lack of standards and protocols for blockchain-based AI systems. The absence of a common framework can make it difficult for different systems to communicate with each other and can lead to interoperability issues.
- Cost: Developing and deploying blockchain-based AI systems can be costly. Companies need to invest in hardware, software, and specialized personnel, which can be a barrier to entry for smaller organizations.
Despite these challenges, the benefits of blockchain-based AI are significant. The combination of these two technologies has the potential to revolutionize industries and transform the way we interact with digital information.
What are the use cases of blockchain-based AI?
Blockchain-based AI is an innovative concept that combines two of the most promising technologies of our time. While still in its early stages, the potential use cases for blockchain-based AI are extensive. Some of the most notable use cases include:
- Secure Data Sharing: One of the most promising applications of blockchain-based AI is secure data sharing. By utilizing blockchain technology to secure data and AI algorithms to analyze it, businesses and individuals can share data in a way that is both secure and transparent.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain-based AI can also be used to improve supply chain management. By using blockchain to track goods and services from production to delivery and AI to analyze the data, businesses can identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement.
- Fraud Detection: Blockchain-based AI can also be used to detect fraud in a variety of industries. By analyzing data from multiple sources and comparing it to known patterns of fraudulent behavior, AI algorithms can quickly identify fraudulent activity.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, blockchain-based AI can be used to securely store and share medical records. This can improve the accuracy of diagnoses and treatment plans, while also ensuring patient privacy and security.
- Smart Contracts: Another promising use case for blockchain-based AI is smart contracts. By using blockchain to create and manage smart contracts, businesses can automate a wide range of processes and transactions, improving efficiency and reducing costs.
- Financial Services: Finally, blockchain-based AI can be used to improve financial services, from banking to insurance. By analyzing large amounts of data in real-time, AI algorithms can identify patterns and trends, helping financial institutions make better decisions and reduce risk.
While blockchain-based AI is still in its early stages, the potential use cases are numerous and varied. As the technology continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see more and more innovative applications emerge.
How high is the potential impact of blockchain-based AI on various industries?
Blockchain-based AI has the potential to revolutionize various industries by enabling secure and decentralized data sharing and collaboration. In the healthcare industry, it could be used to securely store and share patient data, and to improve the accuracy of diagnoses and treatments through AI-powered tools. In the financial industry, it could be used to prevent fraud and improve security in transactions, as well as to create more efficient and transparent payment systems. In the supply chain industry, it could be used to track and verify the authenticity of products, and to improve the efficiency and transparency of logistics. In the energy industry, it could be used to optimize energy consumption and reduce waste through AI-powered analytics.
Overall, the potential impact of blockchain-based AI on industries is significant and diverse, and it has the potential to address many of the challenges and limitations faced by traditional centralized systems. However, it also poses new challenges and requires careful consideration of the ethical and regulatory implications of decentralized and autonomous systems.
This is what you should take with you
- Blockchain-based AI has the potential to transform various industries by combining the strengths of both technologies.
- The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain can help address data privacy and security concerns in AI.
- Blockchain-based AI can also enable the creation of new business models, enhance supply chain management, and facilitate secure and transparent transactions.
- However, there are still challenges and limitations in implementing blockchain-based AI, including scalability and interoperability issues.
- Nevertheless, with ongoing research and development, blockchain-based AI is poised to have a significant impact on the future of technology and society.
What is Random Search?
Optimize Machine Learning Models: Learn how Random Search fine-tunes hyperparameters effectively.
What is the Lasso Regression?
Explore Lasso regression: a powerful tool for predictive modeling and feature selection in data science. Learn its applications and benefits.
What is the Omitted Variable Bias?
Understanding Omitted Variable Bias: Causes, Consequences, and Prevention in Research." Learn how to avoid this common pitfall.
What is the Adam Optimizer?
Unlock the Potential of Adam Optimizer: Get to know the basucs, the algorithm and how to implement it in Python.
What is One-Shot Learning?
Mastering one shot learning: Techniques for rapid knowledge acquisition and adaptation. Boost AI performance with minimal training data.
What is the Bellman Equation?
Mastering the Bellman Equation: Optimal Decision-Making in AI. Learn its applications & limitations. Dive into dynamic programming!
Other Articles on the Topic of Blockchain-based AI
The magazine Forbes also has an interesting article on the the topic.

Niklas Lang
I have been working as a machine learning engineer and software developer since 2020 and am passionate about the world of data, algorithms and software development. In addition to my work in the field, I teach at several German universities, including the IU International University of Applied Sciences and the Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, in the fields of data science, mathematics and business analytics.
My goal is to present complex topics such as statistics and machine learning in a way that makes them not only understandable, but also exciting and tangible. I combine practical experience from industry with sound theoretical foundations to prepare my students in the best possible way for the challenges of the data world.





