Artificial Intelligence (short: AI) describes the attempt to teach a computer human learning and thinking. In contrast to an algorithm, the machine should be able to solve learned tasks for which it was not directly programmed.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
The concept of artificial intelligence has been around longer than most would probably expect. As early as 1950, Alan Turing used the term in his seminar paper “Computing Machinery and Intelligence” and dealt, among other things, with the question of whether machines can think.
He also developed the famous “Turing Test”, which was the first approach to decide whether a computer is “artificially intelligent”. The test setup is relatively simple. A test person asks a second test person and a computer different questions within a certain application area. Afterward, the questioning participant receives the answers without knowing which one comes from a human and which one from a computer.
Now it must try to decide which answer is human and which is not. If it cannot make this assignment correctly in more than 50% of the cases, the computer counts as artificially intelligent, because its answers are considered just as human as those of a human in half of all cases.
Although the work of Turing is considered the cornerstone of the development of artificial intelligence, other definitions have come to the fore in recent years. The book by Stuart Russell and Peter Norvig (Artificial Intelligence, A Modern Approach) has become one of the literary cornerstones.
In this book, the authors define a total of four different goals that artificial intelligence should fulfill in their eyes:
| Human Approach | Ideal Approach |
|---|---|
| Systems that think like people | Systems that think rationally |
| Systems that act like humans | Systems that act rationally |
Regardless of the definition of artificial intelligence, it is a subfield of computer science that uses large data sets and statistical methods to try to learn relationships and apply them to new data.
What are the Types of Artificial Intelligence?
Narrow AI (also known as weak AI or Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)) refers to models that are trained for a specific use case and achieve very good results for it. In this specific area, they can even be better than humans. Most AI systems that already surround us today are classified as Narrow AI. These include, for example, voice systems such as Amazon’s Alexa or Apple’s Siri, as well as driving assistants in autonomous vehicles.
This is contrasted by so-called Broad AI (also known as strong AI or Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)), which is currently still a theoretical phenomenon. This term refers to computers that possess intelligence that is comparable to human intelligence. This would mean that the model could solve a wide variety of applications independently and well while learning at the same time.
Why is Artificial Intelligence important?
There are many areas in which artificial intelligence has already taken on an important role. For example, companies are able to make better decisions, improve their processes and better adapt their products to the wishes of their customers. At the same time, products that use artificial intelligence make our lives easier in many cases, for example in the form of voice assistants, when driving or by making suggestions when shopping.
In general, Artificial Intelligence is important for these reasons, among others:
- Taking over repetitive tasks: Artificial intelligence can not only automate repetitive processes, for example in production but also continuously improve them. Humans can be relieved of these usually tedious tasks and can devote themselves to other tasks.
- Increases utility of existing products: Many applications and products around us have already reached a high level of quality. However, Artificial Intelligence can improve them even further and adapt them to needs. For example, speech systems can increase the usability of cell phones, computers, or even websites by eliminating the need to search for certain functionalities and answer questions directly.
- Use of context from data: The use of artificial intelligence and in particular Deep Learning opens up the possibility of recognizing correlations in large amounts of data and applying them. These can also be relationships that we humans were not even aware of. This generates new knowledge that we can use.
What are Applications of Artificial Intelligence?
Today, we already use a variety of Artificial Intelligence models consciously and unconsciously. The following list is an execution of the most widespread systems:
- Speech recognition: Whether in the car, on the cell phone, or with special devices such as Amazon Alexa, speech recognition is now built into many devices. All kinds of models trained with the help of artificial intelligence serve as the basis.
- Computer vision: The ability of machines to recognize objects or interpret images is also due to artificial intelligence. It is already being used, for example, to make medical diagnoses on the basis of X-rays or to recognize and mark people in pictures.
- Recommendation: Whether on YouTube, e-commerce portals, or Netflix, these providers try to make recommendations that are as precise as possible so that we, as customers, either stay longer on the platform or buy more products. These recommendations are based on various AI algorithms and models.
What are the areas of Artificial Intelligence?
The term Artificial Intelligence is an umbrella term that includes all areas that aim to teach a machine or a computer human behavior. It also includes the area of Machine Learning, which attempts to improve its results step by step with the help of statistical methods, such as Principal Component Analysis or the Decision Tree, and a learning process.

Finally, there is Deep Learning, which is again a subfield of Machine Learning. It uses the structures of a neural network to calculate its results. These multi-layered networks also make it possible to learn significantly more complex relationships than with the simpler models in the field of Machine Learning.
What are the ethical concerns about Artificial Intelligence?
AI has the potential to transform many industries and bring significant benefits to society. However, it also raises ethical concerns that need to be addressed to ensure that AI is used in a responsible and trustworthy manner. Some of the key ethical concerns surrounding AI include:
- Bias: AI systems can be biased if they are trained on data that reflects societal biases, such as race or gender. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, particularly in areas such as hiring, lending, and criminal justice. Addressing bias in AI requires careful attention to data collection and algorithm design, as well as ongoing monitoring and testing to ensure that AI systems are fair and unbiased.
- Privacy: AI systems often require access to large amounts of data, which raises privacy concerns. Personal data can be vulnerable to misuse or theft, and there is a risk that AI systems could be used for surveillance or other purposes that infringe on individual privacy. To address these concerns, AI systems should be designed with privacy in mind, and appropriate safeguards should be put in place to protect personal data.
- Job displacement: As AI systems become more capable of performing tasks that were previously done by humans, there is a risk that they will lead to job displacement. This could particularly affect workers in industries such as manufacturing and transportation. To address this concern, there needs to be a focus on retraining workers and providing them with the skills needed for the jobs of the future.
- Transparency and accountability: AI systems can be opaque and difficult to understand, which raises concerns about accountability and transparency. It can be difficult to determine how decisions are made by AI systems, particularly in cases where they have a significant impact on people’s lives. To address this, there needs to be a focus on developing AI systems that are explainable and transparent, and that can be audited and tested to ensure they are working as intended.
Overall, addressing these ethical concerns is critical to ensuring that AI is used in a responsible and trustworthy manner that benefits society as a whole. By taking a thoughtful and proactive approach to address these concerns, we can help to ensure that AI is used in a way that is fair, transparent, and beneficial to all.
Deep Learning vs. Machine Learning
Deep Learning is a subfield of Machine Learning that differs from Machine Learning in that no human is involved in the learning process. This is based on the fact that only Deep Learning algorithms are able to process unstructured data, such as images, videos, or audio files. Other Machine Learning models, on the other hand, need the help of humans to process this data, telling them, for example, that there is a car in the image. Deep Learning algorithms, on the other hand, can automatically convert unstructured data into numerical values and then incorporate these into their predictions and recognize structures without any human interaction has taken place.
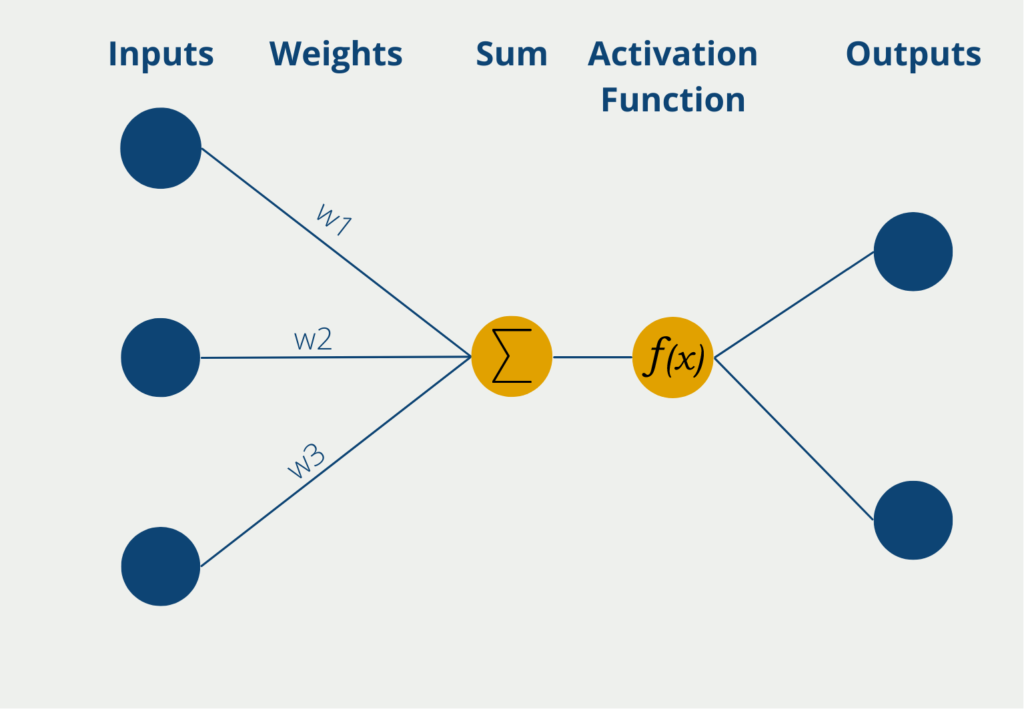
In addition, Deep Learning algorithms are able to process significantly larger amounts of data and thus also tackle more complex tasks than conventional Machine Learning models. However, this comes at the expense of a significantly longer training time for deep learning models. At the same time, these models are also very difficult to interpret. That is, we cannot understand how a neural network arrived at a good prediction.
This is what you should take with you
- Artificial intelligence refers to the attempt to teach computers to think like humans.
- A distinction is made between weak and strong AI. The former refers to models that deliver very good results in individual use cases. Strong AI, on the other hand, is comparable to human intelligence.
- Nowadays, we already encounter artificial intelligence in various applications, such as recommendation systems, speech recognition, or computer vision.
What is a Boltzmann Machine?
Unlocking the Power of Boltzmann Machines: From Theory to Applications in Deep Learning. Explore their role in AI.
What is the Gini Impurity?
Explore Gini impurity: A crucial metric shaping decision trees in machine learning.
What is the Hessian Matrix?
Explore the Hessian matrix: its math, applications in optimization & machine learning, and real-world significance.
What is Early Stopping?
Master the art of Early Stopping: Prevent overfitting, save resources, and optimize your machine learning models.
What is RMSprop?
Master RMSprop optimization for neural networks. Explore RMSprop, math, applications, and hyperparameters in deep learning.
What is the Conjugate Gradient?
Explore Conjugate Gradient: Algorithm Description, Variants, Applications and Limitations.
Other Articles on the Topic of Artificial Intelligence
The following websites provide additional articles on this topic and served as sources:

Niklas Lang
I have been working as a machine learning engineer and software developer since 2020 and am passionate about the world of data, algorithms and software development. In addition to my work in the field, I teach at several German universities, including the IU International University of Applied Sciences and the Baden-Württemberg Cooperative State University, in the fields of data science, mathematics and business analytics.
My goal is to present complex topics such as statistics and machine learning in a way that makes them not only understandable, but also exciting and tangible. I combine practical experience from industry with sound theoretical foundations to prepare my students in the best possible way for the challenges of the data world.





